ESPEI Documentation
ESPEI, or Extensible Self-optimizing Phase Equilibria Infrastructure, is a tool for creating Calphad databases and evaluating the uncertainty of Calphad models. The purpose of ESPEI is to be both a user tool for fitting state-of-the-art Calphad-type models and to be a research platform for developing methods for fitting and uncertainty quantification. ESPEI uses pycalphad for the thermodynamic backend and supports fitting adjustable parameters for any pycalphad model.
ESPEI is developed in the open on GitHub. The project is led by Brandon Bocklund, who is currently a postdoctoral researcher at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Brandon developed ESPEI while completing his Ph.D. under Zi-Kui Liu at The Pennsylvania State University. See the project's History for more details.
What does ESPEI do?
Parameter generation
ESPEI can be used to generate model parameters for Calphad models of the Gibbs energy that follow the temperature-dependent power series expansion of the Gibbs energy within the compound energy formalism (CEF) for endmembers and for binary and ternary Redlich-Kister interaction parameters with Muggianu extrapolation. This parameter generation step augments the Calphad modeler by providing tools for data-driven model selection, rather than relying on a modeler's intuition alone. Model generation is based on a linear regression of enthalpy, entropy, and heat capacity data (see non-equilibrium thermochemical data), using the corrected Akiake Information Criterion (AICc) to prevent overfitting.
Optimization and uncertainty quantification
ESPEI can optimize and quantify the uncertainty of Calphad model parameters to thermochemical and phase boundary data. Optimization and uncertainty quantification is performed using a Bayesian ensemble Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method. Any Calphad database can be used, including databases generated by ESPEI or starting from an existing Calphad database.
ESPEI supports all models supported by pycalphad. User-developed models that are compatible with pycalphad can be used without making any modifications to ESPEI's code. Performing Bayesian parameter estimation for arbitrary multicomponent thermodynamic data is supported.
History
The name ESPEI and early concept were developed by (Shang, Wang, and Liu 2010) under the supervision of Zi-Kui Liu. After developing pycalphad, Richard Otis and Zi-Kui Liu reimagined the concept and wrote pycalphad-fitting (used in (Otis 2016) and (Otis and Liu 2017)), which formed the nucleus for the present version of ESPEI (Bocklund et al. 2019).
Details on the implementation of ESPEI can be found in the following publications:
- B. Bocklund et al., MRS Communications 9(2) (2019) 1–10. doi:10.1557/mrc.2019.59.
- B. Bocklund, Ph.D. Dissertation (Chapter 3), The Pennsylvania State University (2021), https://etda.libraries.psu.edu/catalog/21192bjb54
- B. Bocklund et al., Calphad 86 (2024) 102720. doi:10.1016/j.calphad.2024.102720
We are thankful for the financial support provided to Brandon during his Ph.D. by the Computational Materials Education and Training (CoMET) NSF Research Traineeship (grant number DGE-1449785) and from a NASA Space Technology Research Fellowship (NSTRF, grant number 80NSSC18K1168).
Getting Help
For help on installing and using ESPEI, please join the PhasesResearchLab/ESPEI Gitter room.
Bugs and software issues should be reported on the GitHub issue tracker.
Citing ESPEI
If you use ESPEI for work presented in a publication, we ask that you cite the following publication:
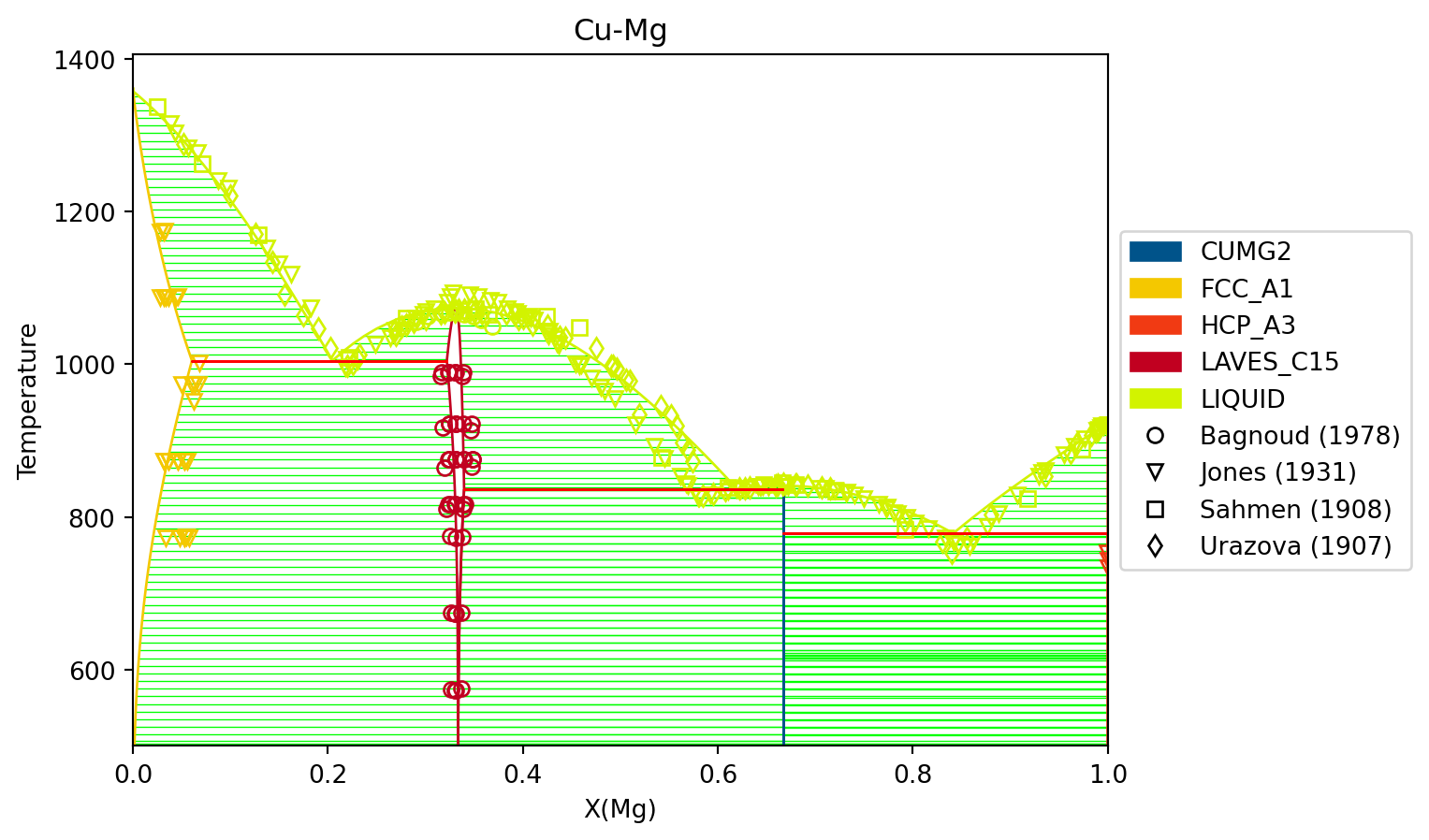
- Bocklund, R. Otis, A. Egorov, A. Obaied, I. Roslyakova, Z.-K. Liu, ESPEI for efficient thermodynamic database development, modification, and uncertainty quantification: application to Cu–Mg, MRS Commun. (2019) 1–10. doi:10.1557/mrc.2019.59.
@article{Bocklund2019ESPEI,
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
arxivId = {1902.01269},
author = {Bocklund, Brandon and Otis, Richard and Egorov, Aleksei and Obaied, Abdulmonem and Roslyakova, Irina and Liu, Zi-Kui},
doi = {10.1557/mrc.2019.59},
eprint = {1902.01269},
issn = {2159-6859},
journal = {MRS Communications},
month = {jun},
pages = {1--10},
title = {{ESPEI for efficient thermodynamic database development, modification, and uncertainty quantification: application to Cu–Mg}},
year = {2019}
}Changelog
See what's new!
License
ESPEI is MIT licensed.
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2015 Richard Otis
Copyright (c) 2017 Brandon Bocklund
Copyright (c) 2018 Materials Genome Foundation
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.